If you are looking for Hernia treatment in Goregaon, you’re likely seeking expert advice, safe surgical options, and an experienced surgeon. A hernia happens when an internal organ or tissue bulges through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle. This can cause a visible lump, discomfort, or pain, especially when bending, coughing, or lifting heavy objects.
A hernia develops when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue wall. The main causes and contributing factors include:
Some people are born with weak abdominal muscles or connective tissue. Others develop muscle weakness over time due to ageing, injury, or previous surgeries.
Muscles may also weaken after surgical incisions, leading to a higher risk, especially for incisional hernias.
Several activities and medical conditions can increase the pressure inside your abdomen, forcing tissue through weak muscle areas:
Lifting heavy objects frequently or improperly.
Chronic or persistent coughing (for example, due to lung conditions or smoking).
Chronic constipation, which leads to straining during bowel movements.
Prostate issues, causing straining to urinate.
Obesity or being overweight, which adds pressure inside the abdomen.
Pregnancy, as growing uterus stretches and weakens the abdominal wall.
Enlarged organs or fluid buildup in the abdomen.
Family history: Genetics and family background may increase risk.
Smoking: Chemicals in tobacco weaken connective tissues and heal wounds poorly.
Poor nutrition: May hinder tissue strength and healing.
Physical exertion: Intense sports or heavy manual labour can trigger hernias.
Previous hernia: Already having a hernia or prior hernia repair increases the chance of recurrence.
Congenital conditions: Babies born prematurely or with low birth weight frequently develop hernias, especially around the belly button.
Women: Pregnancy, childbirth, and hormonal changes can make women more prone to hernias, especially umbilical or femoral types.
Medical conditions: Chronic lung disease, cystic fibrosis, or ongoing peritoneal dialysis.
A hernia usually causes noticeable signs and symptoms, but these can vary depending on the type and location of the hernia. Here are the common symptoms to watch for:
Most hernias create a bulge or lump under the skin, often in the abdomen, groin, or belly button area.
This bulge may become more noticeable when standing up, coughing, bending, or straining.
Sometimes, the bulge can disappear or reduce when lying down or resting.
You might feel a burning, aching, or pulling sensation at the site of the hernia.
Pain often worsens with physical activity, coughing, lifting heavy objects, or straining.
Some people feel a sense of heaviness, pressure, or weakness in the affected area.
The hernia site may swell, and in some cases, especially with inguinal hernias, the bulge can extend into the scrotum in males.
The affected area may feel tender or sore.
Heartburn or acid reflux
Difficulty swallowing
Chest discomfort or burning sensation
Feeling of fullness, burping, or regurgitation of food
Sudden sharp pain at the hernia site
A bulge that becomes red, purple, or dark in color
Nausea or vomiting
Fever
Inability to pass stools or gas
The bulge cannot be pushed back in (incarcerated hernia)
These signs may indicate the hernia is strangulated, meaning the blood supply to the trapped tissue is cut off, which is a medical emergency.
Diagnosing a hernia typically begins with a thorough physical examination by a Dr Pradeep Shriyan, often sufficient to identify the condition. The key steps involved are:
The doctor inspects the suspected area (usually the abdomen, groin, or belly button) for any visible bulges or lumps while you are standing.
You may be asked to cough, strain, or bear down (performing the Valsalva maneuver) to make the hernia bulge more prominent.
The physician may use their hands to gently feel the area and check if any tissue is protruding through the muscle wall.
For groin hernias, the doctor may carefully examine the inguinal canal area and, in men, sometimes invaginate the scrotal skin to feel the hernia through the internal inguinal ring.
Your doctor will ask about symptoms, such as pain, discomfort, or any visible swelling.
They may inquire about factors that could contribute to a hernia, like heavy lifting, chronic cough, constipation, past surgeries, or family history.
While many hernias are diagnosed by physical exam alone, imaging is helpful in uncertain cases, recurrent hernias, or complicated presentations:
Ultrasound:
A safe, non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the abdominal wall and organs. It is especially useful for groin hernias or to differentiate hernias from other conditions. Preferred in children and pregnant women since it involves no radiation.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography):
Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the abdomen and pelvis. It can identify complex hernias and complications like bowel obstruction or strangulation. Contrast dye may be used to enhance the images.
MRI Scan (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
Useful for detailed soft tissue images, especially if sports hernias or groin pain without obvious bulge are suspected. MRI does not use radiation but can detect subtle muscle tears or deep hernias.
Endoscopy and X-rays:
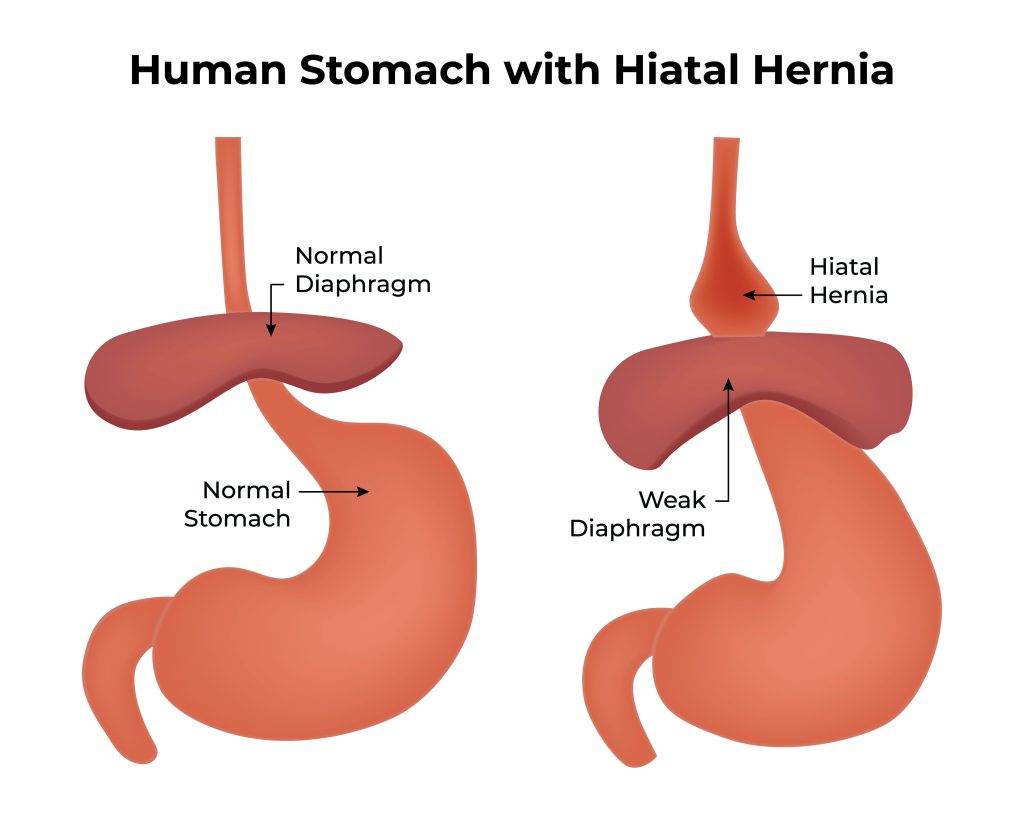
In cases of hiatal hernias (where part of the stomach pushes into the chest cavity), doctors may use an endoscopy or specialized X-rays after swallowing a contrast liquid to visualize the esophagus and stomach.
If the hernia is small and not causing pain or discomfort, doctors may recommend monitoring it without immediate surgery.
Sometimes supportive measures like wearing a truss may help reduce symptoms temporarily, but this is not a permanent solution.
Surgery is the most common and effective treatment for hernias, especially if they are painful, enlarging, or causing complications. The two main surgical approaches are:
The surgeon makes a single incision near the hernia site.
The protruding tissue or organ is pushed back into place.
The weakened muscle wall is repaired by sewing it together.
A mesh (synthetic or biological) is often placed to reinforce the area and reduce chances of recurrence.
This method is suitable for most hernias and is especially preferred for large or complex cases.
Several small incisions are made in the abdomen.
A laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) is inserted to guide the surgery.
Using specialised instruments, the surgeon repairs the hernia with mesh reinforcement.
Benefits include less pain, smaller scars, quicker recovery, and shorter hospital stay.
It is often preferred for bilateral hernias, recurrent hernias after open surgery, or patients who want faster return to activities.
Most hernia repairs today involve using a surgical mesh to strengthen the repair.
Mesh materials can be synthetic or biological and help reduce the recurrence rate.
The choice of mesh depends on hernia type, surgeon preference, and patient factors.
Often managed with medication if symptoms like acid reflux are mild.
Surgery is considered if medications don’t relieve symptoms or complications arise.
Hiatal hernia surgery involves repairing the diaphragm opening and repositioning the stomach using open or laparoscopic techniques.
Early mobilization after surgery is encouraged.
Avoid heavy lifting and straining for several weeks.
Follow-up visits to monitor healing and prevent complications.
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very good Doctor. Friendly and a nice human being. I was in terrible pain due to Fissures since more than a month and went to the doctor requesting for surgery. He explained me everything in best possible way about my problem and answered all my doubts and questions and firmly told me not to opt for surgery telling me surgery is not required. With his medications and advice, I am now feeling much better; pain and uncomfort has drastically reduced and the fissures are almost cured. Thank you so much Doctor Pradeep Shriyan. 🙏 .Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. One of the best Dr I know . He always guides properly.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Good experience & learning as well. I visited to Dr. Pradeep sir for My mother's gall bladder issue/stomach ach. Before visiting to him day before I was taking consultation from other doctor who scared us by telling lot of test. Without proper investigation made our mindset for operation/surgery and he was seems doubtful regarding gall bladder issue. Dr. Pradeep first checked the report clearly and explain us what may be the issue for stomach ach & told that there were no need for operation on such phase. I will suggest if doctor telling multiple and big/major test & operation on first day itself then we need to take consultation from other experienced doctor in that particular field without being panic. His natur of handling patients make us confident and way of talking itself remove our fear.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best dr pradeep shriyan and above all a great human being, full of compassion and personal touch. May God give him strength to heal everyones pain. He is the best surgeon in goregaon.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Doctor Pradeep shreyan excellent doctor 💊🏥 thankyou so much DrTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best & Honest Doctor in Mumbai , Make you feel comfortable , explain you the issues and find the best solution ! High Recommended to all patientsTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. More than doctor he is Good Human Being and Friendly nature. Thank u so much Dr.PRADEEP SHRIYAN SIR.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I met Dr. Pradeep Shriyan for the first time, when my mother was admitted to Jain Hospital, Goregaon-West, for in-patient treatment for Cellulitis, around 7-8 years ago. My impressions about him, from the earliest times are of a well informed, knowledgeable and confident medical professional, who went about his work as a visiting Consultant, with ease, cheer and a smile. Can I ever forget that he treated my mother who was bedridden to be up and about on her feet, in about 8-10 days of hospital stay? Since, then my mother(For her varicose wounds), myself(For routine medical issues), my brother(For a growth on his outer skin) and upon my recommendation, my friends and friend's friends/acquaintances too(For Cancer, Tuberculosis, Digestive Issues, Hernia, etc.) trust and consult the benevolent, kind Dr. Pradeep Shriyan for his valuable advice. To me and my family and friends, Dr. Pradeep Shriyan is not only the best-in-class medical expert but also one of the kindest men I have met. My gratitude to Dr. Pradeep Shriyan and to God for the untold blessings received in medical care and advice through a humane and kind Dr.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. One of the best dr.soft spoken and friendly
Type of surgery: Laparoscopic repair usually costs more due to advanced technology and skill.
Complexity: Larger or recurrent hernias require more time, expertise, and materials.
Hospital facilities and room choice: Private rooms cost more than general wards.
Quality of mesh: Standard or premium-grade mesh options affect the final bill.
Pre- and post-surgery needs: Tests, medications, and follow-up visits add to the cost.
Surgeon’s experience: A skilled, highly reputed surgeon may have higher fees.
Hospital stay duration: Laparoscopic methods often allow faster discharge, reducing stay costs.
Open Hernia Surgery: ₹59,000 – ₹98,000
Mesh Repair (Hernioplasty): ₹75,000 – ₹90,000
Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery: ₹85,000 – ₹110,000
Complex hernia (e.g., large hiatal or incisional): Up to ₹1,50,000
Consultation charges are generally between ₹500 and ₹1,500.
Dr. Pradeep Shriyan, a seasoned and accomplished laparoscopic and general surgeon, is a trusted professional in the Goregaon and nearby area in Mumbai Suburban. With a wealth of experience and expertise, Dr Pradeep Shriyan specialises in a wide range of procedures, including Hernia Treatment in Goregaon, Laparoscopic Hernia surgery in Mumbai, gallbladder stone treatment, piles management, fissure care, fistula interventions, rectal prolapse procedures, and even diabetic foot care management.
Contact us if you are experiencing Appendicitis symptoms. Book an appointment with the Experienced Maestro surgeon, Dr Pradeep Shriyan, in SRV Hospital Goregaon, Mumbai and Dr Pradeep Shriyan (Surana Hospital – Malad), Criticare Asia – Malad
• Have nothing to eat or drink 6 Hours before surgery except for prescribed medications you have been told to take with a sip of water.
• Report 2 hours before the Surgery time (OT Procedure)
• Carry Doctor’s Case Paper on which treatment is written at the time of Admission to Hospital
• Carry Insurance Documents with you to the Hospital before Admission
• Do not apply any lotions, perfumes, deodorants, or Nail polish before surgery
• Take off your jewellery including earrings and piercings
• Don’t shave the area, this will be taken care by Hospital nurse
1. Take pain relieving and other medications as advised. Pain-relieving medication should be taken with food.
2. Follow-up with the doctor after a period of 10 days.
3. Eat a healthy diet and drink plenty of non-alcoholic and non-caffeinated drinks.
4. Do not operate any machinery, or lift any heavy articles after Surgery
5. Rest for a few days after the surgery is advisable, but keep mobile.
6. Avoid Bath till the dressing and stiches gets dissolve
Please consult doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
• Increased drainage from the incision (Operated area)
• Increased redness around the operated area
• Large amount of swelling under the wound
• Foul odour from operated area
• Fever greater than 38.0 degrees C.
• Sudden calf pain or shortness of breath
Developed by PRAZONE Web Solutions
Copyright © 2024 All rights reserved by
Dr Pradeep Shriyan